




Abstract:
Schmid G., Pecqueur S., Halik M.

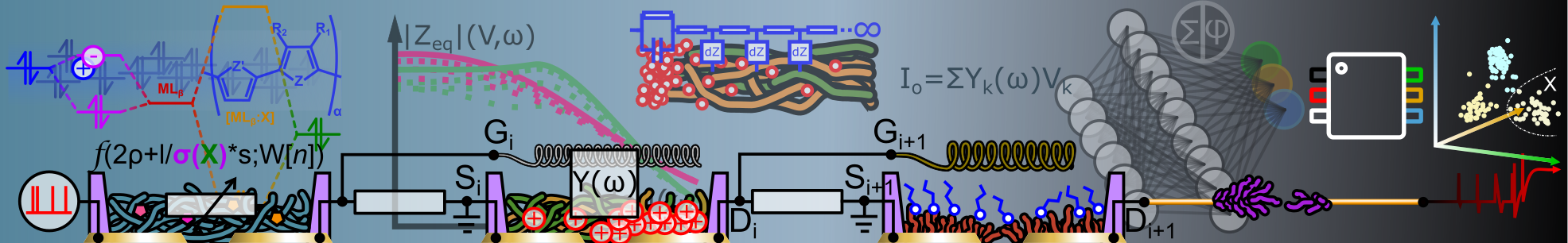
 Abstract: New classes of conductivity doping materials for organic electrical devices, especially lightemitting diodes, have been identified in this study. Conductivity, mobility and charge-carrier density determination was presented with the example of aluminium tris(8-hydroxyquinolate) n-doping, co-evaporated with caesium orthovanadate, a new n-doping material. The refinement of the calculated conductivity and the verification of charge-carrier density were provided via other independent and published methods. The confirmation certified the accuracy of the obtained values, and the methods were used for the characterisation of further dopants and their doping strength. Struture-property relashionships were carried out from the investigation of doping materials at their chemical level and their electrical behaviour. Systematic p-doping studies of different organometallic Lewis acid complexes in different hole transport materials at different dopant concentrations were performed. First of all, the investigation by the metal centres variation of the three paddlewheel dichromium(II,II)-, dimolybdenum(II,II)- and dirhodium(II,II)-trifluoroacetate complexes exhibited the dependency of the p-doping strength with the electrophilily of the core. A ligand variation stu dy over 10 bismuth(III)-carboxylate complexes demonstrated the electron-withdrawing effect of the ligand to be responsible for the enhancement of the p-doping effect in the complex. The conductivity of different hole transporters, doped with different bi smuth dopants, was correlated to the change of dipole moment, pKa and Hammett parameter of the carboxylic acid ligands. From these correlations, Linear Free-Energy Relationships showed the donor/acceptor interaction between the dopant and the semiconduct or to obey a Lewis acid/base equilibrium (hybrid charge-transfer complex formation) rather than on a redox equilibrium (integer charge-transfer complex formation). One of the p-dopants was chosen as replacement in thick hole transport layer of white orga nic light-emitting diodes and showed comparable or better effects on the devices than a reference, doped with a commercially available p-dopant. It demonstrates the potential use of these Lewis acidic p-dopants for other opto-electronic applications in a n organic semiconductor based devices.
Abstract: New classes of conductivity doping materials for organic electrical devices, especially lightemitting diodes, have been identified in this study. Conductivity, mobility and charge-carrier density determination was presented with the example of aluminium tris(8-hydroxyquinolate) n-doping, co-evaporated with caesium orthovanadate, a new n-doping material. The refinement of the calculated conductivity and the verification of charge-carrier density were provided via other independent and published methods. The confirmation certified the accuracy of the obtained values, and the methods were used for the characterisation of further dopants and their doping strength. Struture-property relashionships were carried out from the investigation of doping materials at their chemical level and their electrical behaviour. Systematic p-doping studies of different organometallic Lewis acid complexes in different hole transport materials at different dopant concentrations were performed. First of all, the investigation by the metal centres variation of the three paddlewheel dichromium(II,II)-, dimolybdenum(II,II)- and dirhodium(II,II)-trifluoroacetate complexes exhibited the dependency of the p-doping strength with the electrophilily of the core. A ligand variation stu dy over 10 bismuth(III)-carboxylate complexes demonstrated the electron-withdrawing effect of the ligand to be responsible for the enhancement of the p-doping effect in the complex. The conductivity of different hole transporters, doped with different bi smuth dopants, was correlated to the change of dipole moment, pKa and Hammett parameter of the carboxylic acid ligands. From these correlations, Linear Free-Energy Relationships showed the donor/acceptor interaction between the dopant and the semiconduct or to obey a Lewis acid/base equilibrium (hybrid charge-transfer complex formation) rather than on a redox equilibrium (integer charge-transfer complex formation). One of the p-dopants was chosen as replacement in thick hole transport layer of white orga nic light-emitting diodes and showed comparable or better effects on the devices than a reference, doped with a commercially available p-dopant. It demonstrates the potential use of these Lewis acidic p-dopants for other opto-electronic applications in a n organic semiconductor based devices.
© 2019-2025 Sébastien Pecqueur